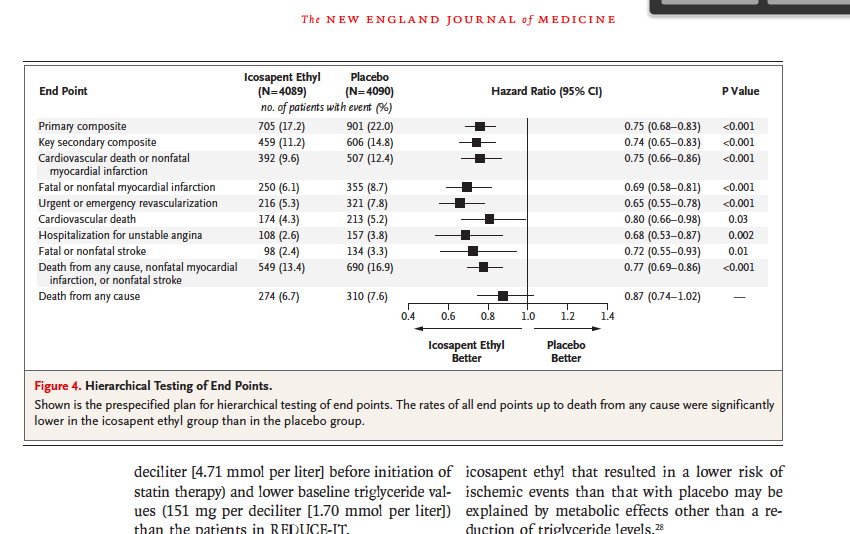
In other words, the relative reduction in risk of death is always less than the hazard ratio implies It is also a decreasing function of the time point at which it is assessed For instance, in the example in Figure 1 , a 40% hazard reduction implies risk reductions of 25% and only 14% in the 1year and 2year mortality rates, respectivelyThere can be substantial difference in the association of a risk factor with prevalent disease versus ;The risk difference of A relative to B is 001, the risk ratio is 101 Or one could view the risk ratio and the odds ratio as approximations to the hazard ratio or rate ratio Rates and hazards can exceed 1, unlike risks, so there's no constraint on the hazard ratio, unlike the risk ratio
Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube
Hazard ratio vs relative risk vs odds ratio
Hazard ratio vs relative risk vs odds ratio-Odds ratio vs Relative Risk/Hazard Ratio I have a background in physics with a few courses in statistics, but I still have a hard time intuitively understanding OR I get RR as it just is a ratio of probabilities, and I look at HR as RR with a time component RR Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent a risk ratio, ;



Individual And Community Level Risk For Covid 19 Mortality In The United States Nature Medicine
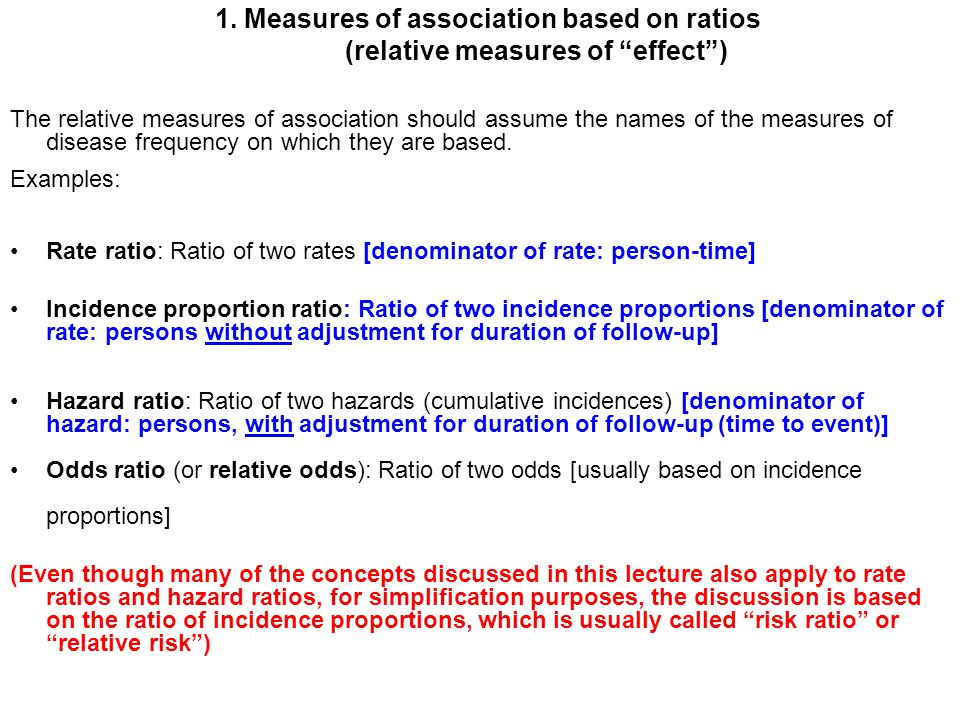
A rate ratio, ; The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programA prevalence ratio, or ;
Even an odds ratio;RR and OR are commonly used measures of association in observational studies In this video I will discuss how to interpret them and how to apply them to patIn the general medical literature, rate is often incorrectly used for prevalence measures
Odds are the ratio of the probability of an ev ent occurring in a group, divided by the probability of that ev ent not occurring odds = π 1 − π For example, if probability of death in aThe Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed toThis is not true for relative risk Switching the rows or columns inverts the odds ratio For example, the odds ratio for no cough given a history of bronchitis = (247/26)/(1002/44) = 0417 = 1/2397 This is the reciprocal of the OR for cough There are only two possible odds ratios, as switching both rows and columns gives




Odds Ratios And Log Odds Ratios Clearly Explained Youtube




Statistics For Afp Dr Mohammad A Fallaha Afp
Sometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should findOdds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of odds I just remember that odds ratio is a ratio of odds and probability isn't a ratio of odds (AKA it is the other option) Relative Risk = Probability / Probability Odds Ratio = Odds / Odds Now that you have a general idea of what odds ratio and relative risk are you need to know when to use




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube
Odds that a person with an adverse outcome was at risk (or exposed)/ Odds that a person without an adverse outcome was at risk (or exposed) Odds group 1/odds group 2Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratio Note that the relative risk and the incidence rate ratio were different, 058 versus 042, with the timedependent relative risk suggesting a greater benefit from intervention than the overall relative risk, and which is also fairly close to the estimated hazard ratio of 039 (row j)




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar



Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar
Relative risk vs Odds Ratio vs Hazard Ratio Relative risk and risk ratios (probabilitiy ratios) are different from odds ratios, although they might be close in certain cases Even though odds ratios have more practical applications, relative risk is arguably a more intuitive measure of effectiveness and so has its applications in fields likeLet us now look at the relation between the relative risk and the odds ratio (Zhang and Yu, 1998) OR= ˇ 1 1 1ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 = ˇ ˇ 2 1 2 1 1 = RR 2 1 (21) From this we see that OR is always further away from 1 than RR But, more importantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998) A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidence intervals 26 , 32



Hazard Ratio Calculator Calculate Hazard Ratio Hr Confidence Intervals P Value




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1
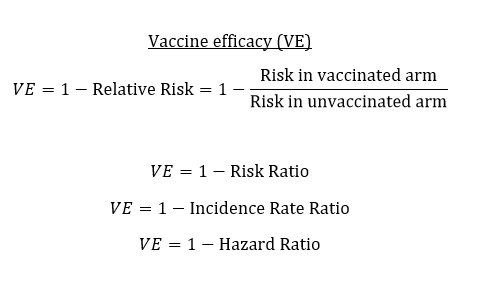
The size of your absolute risk reduction depends on what your risk is to begin with Hazard Ratios Doctors sometimes use the term "hazard ratio" to talk about risk A hazard ratio considers your absolute risk to be 1 If something you do or take doesn't change your risk, then the hazard ratio is 1 If something you do or take lowers your risk Hazard Ratio (ie the ratio of hazards) = Hazard in the intervention group ÷ Hazard in the control group Hazard represents the instantaneous event rate, which means the probability that an individual would experience an event (eg death/relapse) at a particular given point in time after the intervention, assuming that this individual has survived to that particular point of timeVariable on the hazard or risk of an event Hazard ratio can be considered as an estimate of relative risk, which is the risk of an event (or of developing a disease) relative to exposureRelative risk is a ratio of the probability of the event occurring in the exposed group versus the control (nonexposed) group



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Individual And Community Level Risk For Covid 19 Mortality In The United States Nature Medicine
When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators Or one could view the risk ratio and the odds ratio as approximations to the hazard ratio or rate ratio Rates and hazards can exceed 1, unlike risks, so there's no constraint on the hazard ratio, unlike the risk ratio Hazard ratios / rate ratios can therefore be constant over the entire range of baseline hazard / background rate Roger




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia
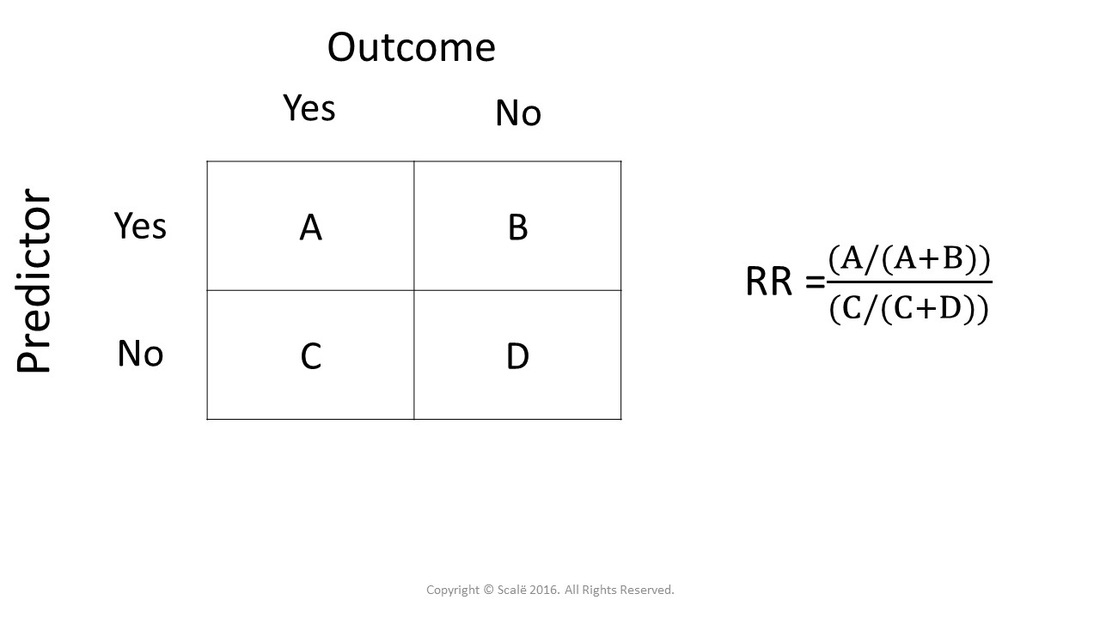
The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to theA risk ratio of 10 indicates identical risk among the two groups A risk ratio greater than 10 indicates an increased risk for the group in the numerator, usually the exposed group A risk ratio less than 10 indicates a decreased risk for the exposed group, indicating that perhaps exposure actually protects against disease occurrenceThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a ) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions Neither the risk ratio nor the odds ratio can be calculated for a study



2




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar
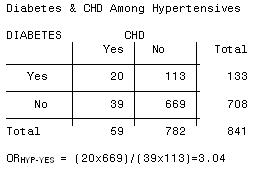
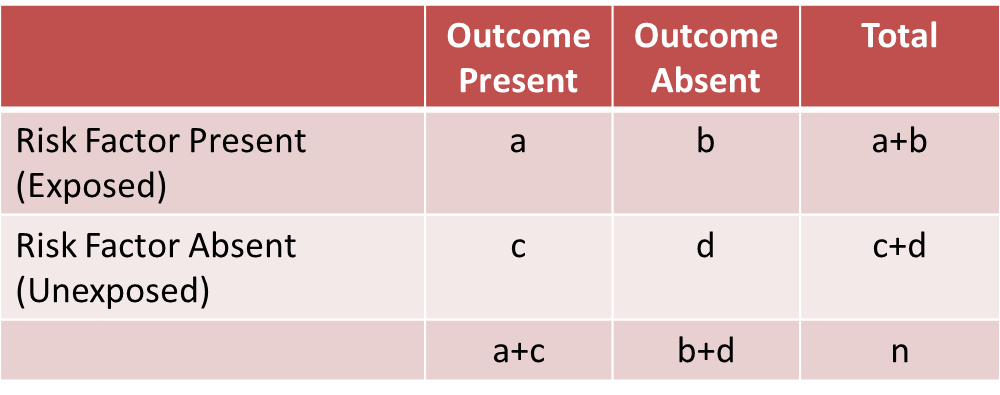
The odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies Hazard ratios differ from relative risks (RRs) and odds ratios (ORs) in that RRs and ORs are cumulative over an entire study, using a defined endpoint, while HRs represent instantaneous risk over the study time period, or some subset thereof Hazard ratios suffer somewhat less from selection bias with respect to the endpoints chosen and can indicate risksAn odds ratio is simply the ratio of two sets of odds Increasing the odds ratio while holding a base odds constant corresponds to increasing the other odds, but may or may not be similar to the relative change in probability You may also want to ponder the difference between hazard and probability (see my earlier discussion where I make mention of handwaving;What does a relative risk



2




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk
Odds ratios approximate risk ratios when the outcome under consideration is rare but can diverge substantially from risk ratios when the outcome is common In this paper, we derive optimal analytic conversions of odds ratios and hazard ratios to risk ratios that are minimax for the bias ratio when outcome probabilities are specified to fall inExcept for this difference the hazard ratio is expressed much in the same way as the relative risk A hazard ratio of 1 would indicate that there was no difference between treatments, whereas a hazard ratio of 2 would signify that the treatment group had twice the rate of an event, and a hazard ratio of 05 would signify that the treatment Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome Methods Casecontrol studies are quite common in medical studies Hazard ratio (HR) is nearly the same measure often quoted Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent



State The Mean Median Hr Hazard Ratio Chegg Com




Hazard Ratios And Survival Curves Youtube
Odds ratio OR = (odds of disease in exposed) / (odds of disease in unexposed) Both RR and OR are estimates from samples, and they are continuous measures In order to assess the potential for random error, it is important to assess the precision of these estimates with a confidence interval, but there is a problem in that these measures areRelative risks, odds ratio, hazard ratio relative risk/risk ratioratio of risk of an event occuring in the exposed group vs the unexposed grouprisk exposed risk unexposed RR Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a



Plos One Bleeding Risk With Long Term Low Dose Aspirin A Systematic Review Of Observational Studies




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)Relative risk, odds ratio and hazard ratio (and their confidence intervals) will be less than 10 If the converse holds true, these values will be greater than 10 Key words clinical trials, number needed to treat, odds, statistics (Aust Prescr 08;3112–16) Introduction Introduction and background Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results 1 A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
Essentially, the odds ratio estimate the _______ in these types of studies Risk ratio What is the definition of odds ratio?Percent, population attributable risk percent, relative risk, odds, odds ratio, and others The concept and method of calculation are explained for each of these in simple terms and with the help of examples The interpretation of each is presented in plain English rather than in technical language Clinically useful notes are provided, If the risk ratio is 1 (or close to 1), it suggests no difference or little difference in risk (incidence in each group is the same) A risk ratio > 1 suggests an increased risk of that outcome in the exposed group A risk ratio < 1 suggests a reduced risk in the exposed group Percent Relative




Hazard Ratio Wikipedia




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube
Absolute risk refers to the simple event rate in a group of people who receive an intervention (see Example 1) Relative risk (RR) estimates the size of effect of an intervention of interest relative to the size of effect of a comparator (see Example 2) Absolute risk reduction(ARR) is the difference in event rates between two interventions To beAn odds ratio is simply the ratio of two sets of odds Increasing the odds ratio while holding a base odds constant corresponds to increasing the other odds, but may or may not be similar to the relative change in probability You may also want to ponder the difference between hazard and probability (see my earlier discussion where I makeThe relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other group



Know The Nuances Of Vaccine Efficacy When Covering Covid 19 Vaccine Trials Association Of Health Care Journalists




How Did Researchers Calculate The Hazard Ratio Cross Validated
The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either ofIn a cohort study, particularly on the occasion of a logistic regression, we replace the relative risk by the odds ratio if the disease is rare (incidence less than 10%)Hazard ratio The hazard ratio in survival analysis is the effect of an exploratory?




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
The relative risk has a similar property except that it cannot remain constant across all control group probabilities, a relative risk of 2 is only possible for a control group probability $\leq 50\%$ and so do the hazard ratio, as well as the rate ratio



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



Relative Risk




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research



Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Statistics For Gp And The Akt Sept 11




Estimated Relative Risk Odds Ratio Or Hazard Ratio With 95 Ci For 4 Download Scientific Diagram




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Hazard Ratios




Nonproportional Hazards For Time To Event Outcomes In Clinical Trials Jacc Review Topic Of The Week Sciencedirect




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Hazard Ratio Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio Of Selected Outcomes For The Download Table



What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf



3 5 Bias Confounding And Effect Modification Stat 507




Hazard Ratio An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




In A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Estimates From Observational Studies Can I Pool Or With Hr And Rr Probably Not How Can I Transform Hr To Or




Odds Ratio Litfl Ccc Research



Hazard Ratio




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy



1




Pdf Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




Graph Tip How Can I Plot An Odds Ratio Plot Also Known As A Forest Plot Or A Meta Analysis Plot Faq 809 Graphpad




Eposters How Big Is A Big Hazard Ratio




Applied Interpretation Of Clinical Studies Jim Hoehns Pharm D ps Fccp Ppt Download




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




Odds Ratio Article




Graphical Presentation Of Relative Measures Of Association The Lancet




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Measures Of Association Ppt Download



A Stratified Analysis




Ppt Measures Of Association Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Epidemiologic And Research Applications In Community Nursing Lecture




Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect




Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar



How To Read A Forest Plot Cochrane Uk



Hazard Ratio Vs Odds Ratio ただの悪魔の画像




Lincom Stata




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




Design And Analysis Of Clinical Study Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Dr Tuan V Nguyen Garvan Institute Of Medical Research Sydney Australia Ppt Download




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




Interpreting Hazard Ratios Youtube




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Frontiers Odds Ratio Or Prevalence Ratio An Overview Of Reported Statistical Methods And Appropriateness Of Interpretations In Cross Sectional Studies With Dichotomous Outcomes In Veterinary Medicine Veterinary Science




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




Flowchart Of Study Selection Process Hr Hazard Ratios Or Odds Download Scientific Diagram



1



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia




Cecile Janssens A Reminder That Odds Ratios Massively Overestimate Relative Risks When Outcome Is Common In The Population Or By Study Design E G Case Control Studies Io Is Proportion Of Cases




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Measures Of Association Ppt Download



Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey




A Meta Analysis Of Adjusted Hazard Ratios From Observational Studies Of Bilateral Versus Single Internal Thoracic Artery Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting Sciencedirect




Research Techniques Made Simple Interpreting Measures Of Association In Clinical Research Sciencedirect




Tutorial About Hazard Ratios Students 4 Best Evidence



How To Explain The Difference Between Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk To A Layman Quora



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Confidence Intervals And P Values



Hazard And Hazard Ratio In Statistics



How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Janez Stare Semantic Scholar




Fillable Online Odds Ratio Hazard Ratio And Relative Risk Fax Email Print Pdffiller



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿